Tongan (Faka-Tonga)
Tongan is a member of the Polynesian branch of the Austronesian languages
spoken by about 95,000 people mainly in Tonga. It is also spoken in American
Samoa, Australia, Canada, Fiji, New Zealand, Niue, the USA and Vanuatu. It
closely related to Niue, Wallisian and Samoan.
Tongan was first written by missionaries in the early 19th century using
a number of different spelling systems. The currect system was promulgated
by the Privy Council of Tonga in 1943.
Tongan alphabet (Ko e motu’alea Tonga)
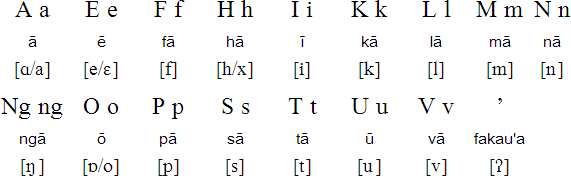
Notes
- A macron (ā, ē, etc.) lengthens a vowel.
- There are no consonant clusters or diphthongs in Tongan (ng is considered a letter, so it is not an exception).
- All letters are fully voiced.
Sample text in Tongan
Ko e kotoa ‘o ha’a tangata ‘oku fanau’i mai ‘oku tau’ataina pea tatau ‘i he
ngeia mo e ngaahi totonu. Na’e fakanaunau’i kinautolu ‘aki ‘a e ‘atamai mo e
konisenisi pea ‘oku totonu ke nau feohi ‘i he laumalie ‘o e nofo fakatautehina.
Translation
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They
are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another
in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
