 Phags-pa script
Phags-pa script
In 1260 Kublai Khan commissioned a Tibetan Lama called Blo-gros
rGyal-mtshan, who is better known by the title Phags-pa Lama,
to create a new national script to replace the Uighur-based
script, which was devised in 1208. An edict was issued in 1269 requiring
the use of the new script in all official documents, along with the local
script as appropriate.
The old Mongolian script was thought unsuitable because it was borrowed
from the Uighurs rather than being a unique Mongol creation; and because it
didn’t do a very good job of representing the sounds of Mongolian, let only
other languages such as Chinese. It is probable that Kublai Khan hoped that
the new script would be used to write all the languages spoken within his
empire, and he ordered the establishment of schools to teach the new script.
The script was originally called “Mongolian new letters” – 蒙古新字
(měnggǔ xīnzì) in Chinese, a name still used in
Tibetan. However the script is now known as dörbelǰin üsüg,
square script, in Mongolian and as 八思巴字
(bāsībā zì), Phags-pa letters, in Chinese. In English
the script is referred to as the Mongolian Quadratic Script, or more
commonly, the Phags-pa scipt, a name with many variant spellings.
The Phags-pa script did not prove popular with Mongolian and Chinese
officials, who used the new script only to a limited extent and reluctantly.
The many edicts prohibiting use of the older Mongolian script had little
effect. Usage of the script among private individuals was even more limited.
The Chinese abandoned the script completely after the Yuan Dynasty collapsed
in 1368, while the Mongols reverted to their Uighur-based script.
The most recent example of Phags-pa writing in Mongolian dates from 1352,
though there are some later examples in Chinese. However the script is still
used occasionally in Tibetan for decorative purposes on seals and temple
inscriptions. It is also used to write some business names in Mongolia.
Notable features
- Type of writing system: syllabic alphabet – each consonant includes
an inherant vowel sound, a. Other vowels are indicated by symbols that
appear below the consonants. - Writing direction: vertical from top to bottom and from left to right.
- There were three different styles of writing in the Phags-pa alphabet:
the Standard script, which was used in Chinese and Mongolian printed texts
and documents; the Seal script, which was used mainly for official seals,
and also for some inscriptions on monuments; and the Tibetan script style,
which was used mainly for books titles and temple inscriptions.
Used to write
Mongolian, Chinese, Tibetan and Sanskrit.
Phags-pa alphabet (Standard script)
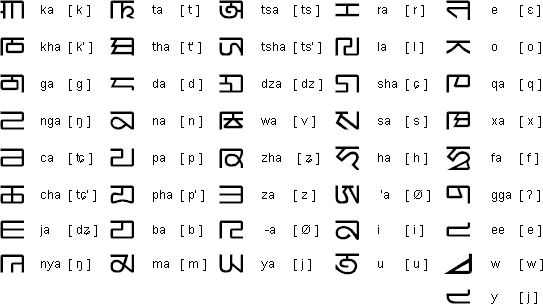
Source: http://www.babelstone.co.uk/Phags-pa/41Letters.html
Phags-pa alphabet (Seal script style)

Phags-pa alphabet (Tibetan script style)

Sample text in Phags-pa (Standard script style)

Part of the 1345 Phags-pa Sanskrit inscription at Juyongguan
Source: http://babelstone.blogspot.com/
Links
Free Phags-pa fonts
http://www.babelstone.co.uk/Fonts/
http://www.valdyas.org/conlang.html
Further information about the Phags-pa Script
http://www.babelstone.co.uk/Phags-pa/
