Lontara
The Lontara script is descended from the Brahmi
script of ancient India. The name lontara derives from the Malay
word for the palmyra palm, lontar, the leaves of which are the
traditional material for manuscripts in India, South East Asia and Indonesia.
Notable features
- Type of writing system: syllabic alphabet / alphasyllabary
- Direction of writing: left to right in horizontal lines
- In common with other Brahmi-derived
syllabic alphabets, each consonant has an inherent vowel [a], other
vowels are indicated by adding diacritics above or below a consonant.
Used to write:
Bugis or Buginese (ᨅᨔ ᨕᨘᨁᨗ),
Makassarese (ᨅᨔ ᨆᨀᨔᨑ) and Mandar,
Austronesian languages spoken on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi.
Both scripts were once used to write laws, treaties, maps, etc in Bugis,
but are now only used for marriage ceremonies. The Makasar script is
still widely used to write Makasar, although the Latin
alphabet is officially favoured.
Lontara script for Bugis
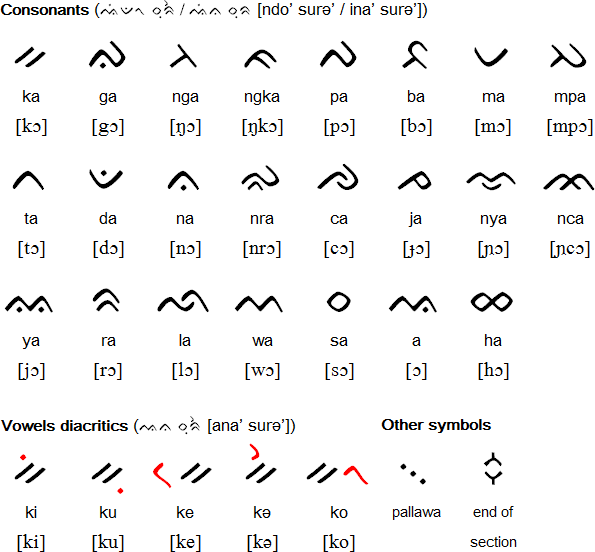
Consonants
Vowels
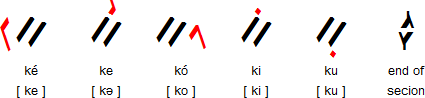
Sample text in the Lontara script in Bugis

Sample text in Bugis (Latin alphabet)
Sininna rupa tau ri jajiangngi rilinoe nappunnai manengngi riasengnge
alebbireng . Nappunai riasengnge akkaleng, nappunai riasengnge ati
marennni na sibole bolena pada sipakatau pada massalasureng.
Translation
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with
reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
Links
Information about Buginese, Lontara and Makassarese
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buginese_language
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lontara
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Makassarese_language
Free Lontara font
http://alibataatpandesal.com/outbox.html
