Khahabran
The Khahabran alphabet was created by David Hunt
(kennymimi@bellsouth.net)
in order to write Makharian, a constructed language inspired by
Latin and Turkish. The Eastern feel of the alphabet is meant to
be reminiscent of the Byzantine Empire where David’s own Makhar
Empire is based.
Internal history
The language is a branch of the Makharian limb of the Sethrë
language group, the most common of the Anyarë tongues. Khahabran
is the informal tongue of the Makhar Empire, a lingua franca
of sorts, Makharian being the formal speech, the lingua nobis.
Created by the scholar Arhamidel al-Vyryk, Emperor Geminnius XVIII
declared it the official alphabet in the year 1523 of the Second Dynasty.
The New Khahabran Alphabet replaced the old ideograms of the Auric
languages, which was difficult to master and cumbersome to write.
The alphabet was, surprisingly, built around the old ideograms,
which had also had a phonetic alphabet in order to easily translate
other languages.
Notable features
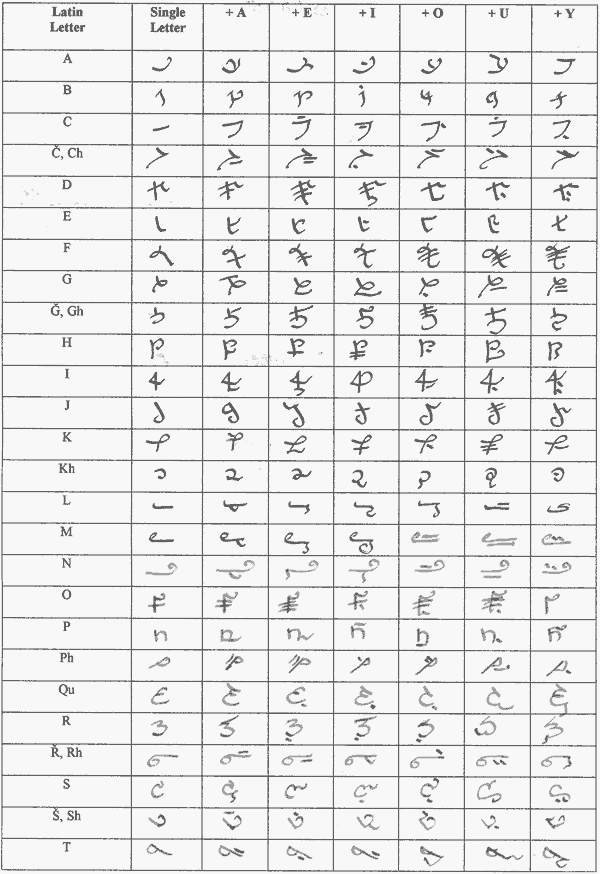
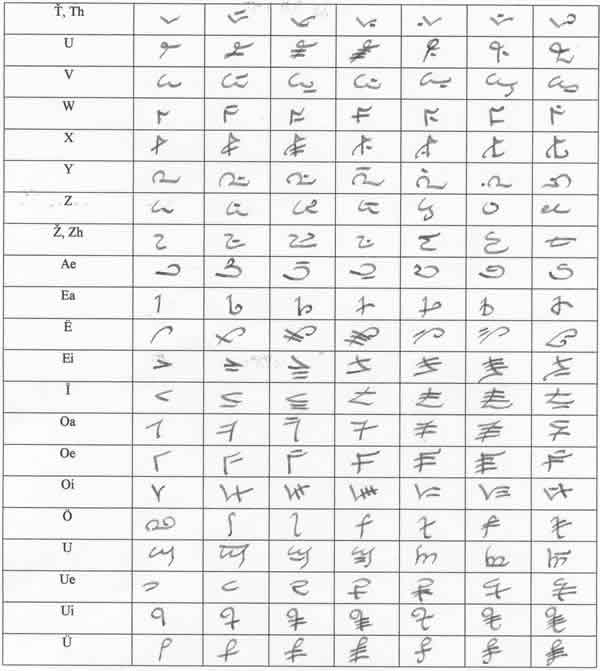
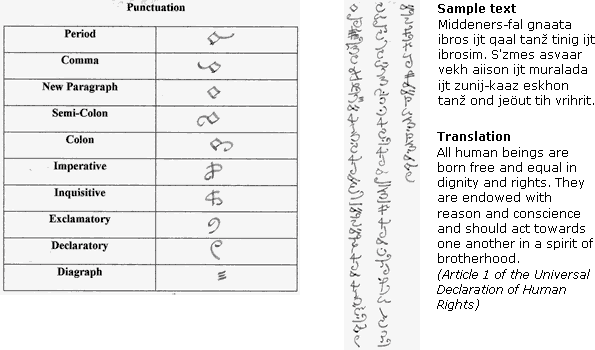
- The Khahabran alphabet is written vertically from top to bottom and
from left to right. - It can be used to write a multitude of languages.
- The alphabet is quite suitable for calligraphy; it can be written
using a brush or pen. - The alphabet is built around vowels. Every letter is built around
seven forms; single letter, letter + A, letter + E, letter + I, letter + O,
letter + U, and letter + Y. This makes it a pseudo-syllabic alphabet,
though Makharian can be classified as an abjad.
Khahabran alphabet